Now a Southern Cross provider!
Sleep? Ain't no body got time for that!
If you’ve ever spent a night tossing and turning, you already know how you’ll feel the next day — tired, cranky, and out of sorts. But missing out on the recommended 7 to 9 hours of shut-eye nightly does more than make you feel groggy and grumpy.
The main symptom of ongoing sleep loss is excessive daytime sleepiness, but other symptoms include:
yawning
moodiness
fatigue
irritability
depressed mood
difficulty learning new concepts
forgetfulness
inability to concentrate or a "fuzzy" head
lack of motivation
clumsiness
increased appetite and carbohydrate cravings
The long term effects of sleep deprivation are real. It drains your mental abilities and puts your physical health at real risk. Science has linked poor slumber with all kinds of health problems, from weight gain to a weakened immune system.
Memory Issues: During sleep, your brain forms connections that help you process and remember new information. A lack of sleep can negatively impact both short and long-term memory.
Trouble with thinking and concentration: Your concentration, creativity and problem-solving skills aren’t up to par when you don’t get enough rest.
Mood changes: Sleep deprivation can make you moody, emotional, and quick-tempered. Chronic sleep deprivation can affect your mood and lead to anxiety or depression, which may escalate. reduced tendency to think positively, bad moods, a decreased willingness to solve problems, intolerance and less empathy toward others, poor impulse control, inability to delay gratification.
Weakened immunity: Studies show that people who don't get quality sleep or enough sleep are more likely to get sick after being exposed to a virus, such as a common cold virus. Lack of sleep can also affect how fast you recover if you do get sick. During sleep, your immune system releases proteins called cytokines, some of which help promote sleep. Certain cytokines need to increase when you have an infection or inflammation, or when you're under stress. Sleep deprivation may decrease production of these protective cytokines. In addition, infection-fighting antibodies and cells are reduced during periods when you don't get enough sleep.
Accidents: being drowsy during the day can increase your risk for car accidents and injuries from other causes.
High Blood pressure: If you sleep less than five hours a night, your risk for high blood pressure increases.
Risk of heart disease: Sleep deprivation may lead to increased blood pressure and higher levels of chemicals linked to inflammaction, both of which play roles in heart disease.
Risk of diabetes: A lack of sleep affects your body’s release of insulin, a blood sugar-lowering hormone. People who don’t get enough sleep have higher blood sugar levels and an increased risk for type 2 diabetes.
Weight gain: With sleep deprivation, the chemicals that signal to your brain that you are full are off balance. As a result, you’re more likely to overindulge even when you’ve had enough to eat. It's believed to be because sleep-deprived people have reduced levels of leptin (the chemical that makes you feel full) and increased levels of ghrelin (the hunger-stimulating hormone).
Low sex drive: People who don’t get enough sleep often have a lower libido. In men, this decreased sex drive may be due to a drop in testosterone levels.
HOW MUCH SLEEP DO WE NEED?
The National Sleep Foundation (NSF) 2015 recommendations for appropriate sleep durations for specific age groups are:
Newborns (0 to 3 months): 14 to 17 hours each day
Infants (4 to 11 months): 12 to 15 hours
Toddlers (1 to 2 years): 11 to 14 hours
Preschoolers (3 to 5 years): 10 to 13 hours
School-age children (6 to 13 years): 9 to 11 hours
Teenagers (14 to 17 years): 8 to 10 hours
Adults (18 to 64 years): 7 to 9 hours
Older adults (over 65 years): 7 to 8 hours
Most of us need around 8 hours of good-quality sleep a night to function properly – but some need more and some less. What matters is that you find out how much sleep you need and then try to achieve it.
As a general rule, if you wake up tired and spend the day longing for a chance to have a nap, it's likely that you're not getting enough sleep.
A variety of factors can cause poor sleep, including health conditions such as sleep apnoea. But in most cases, it's due to bad sleeping habits.
HOW TO CATCH UP ON LOST SLEEP?
If you don't get enough sleep, there's only one way to compensate – getting more sleep.
It won't happen with a single early night. If you've had months of restricted sleep, you'll have built up a significant sleep debt, so expect recovery to take several weeks.
Starting on a weekend, try to add on an extra hour or 2 of sleep a night. The way to do this is to go to bed when you're tired, and allow your body to wake you in the morning (no alarm clocks allowed!).
Expect to sleep for upwards of 10 hours a night at first. After a while, the amount of time you sleep will gradually decrease to a normal level.
Don't rely on caffeine or energy drinks as a short-term pick-me-up. They may boost your energy and concentration temporarily, but can disrupt your sleep patterns even further in the long term.
HOME MANAGEMENT
The good news is that most of the negative effects of sleep deprivation reverse when sufficient sleep is obtained. The treatment for sleep deprivation is to satisfy the biological sleep need, prevent deprivation and "pay back" accumulated sleep debt.
Some suggestions for good sleep habits include:
going to bed when tired
following a routine for bed and wake-up times, keeping it consistent every day of the week
avoiding eating 2 to 3 hours before bedtime
if unable to fall asleep after 20 minutes of trying, going to another room and trying to read until feeling sleepy, then returning to bed
engaging in regular exercise during the day
keeping the bedroom quiet, dark and a comfortably cool temperature
turning off electronic devices when you go to bed
EVERYONE NEEDS A BUTT MASSAGE. Part 2
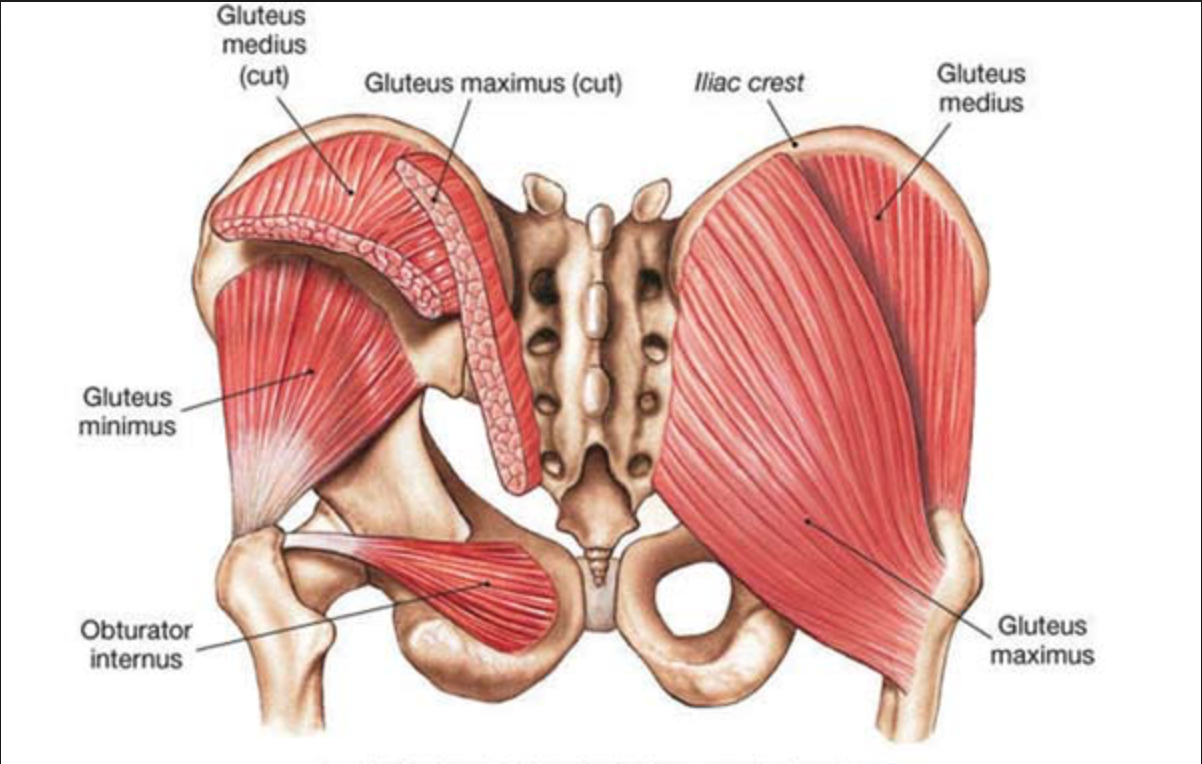
Ahhhh, the gluteus medius. AKA: the glute med!
Unless you are a runner, ballet dancer or a yogi, you probably have never heard of this muscle before.
It is one of the three gluteus muscles, along with the gluteus maximus and minimus and originates on the outer surface of the ilium (pelvis) just below the iliac crest and converges as a large flattened tendon onto the lateral greater trochanter of the femur (thigh bone).
AND WHAT IS the FUNCTION of the glute med?
The main function of the glute med is abduction of the hip. Abduction is when you move the leg away from the center of the body. Is also responsible for external rotation of the hip when the hip is extended and internal rotation of the hip when it is flexed…more accurately; it prevents external rotation when flexed.
But, the most important job of the glute med is stabilization of the pelvis. Activation of the muscle prevents dropping of the pelvis when standing on one leg. When the glute med is injured or weak, it allows the opposite hip to drop when weight bearing on one leg such as when walking or running.
It also helps your bigger gluteus maximus muscle flex and extend your leg. Having strong glutes is important because we use our glutes in everyday life when you push off the ground while walking, running, or stepping.
WHAT HAPPENS IF the gluteus med IS DISFUNCTIONAL?
When the gluteus medius does not function well, there are implications down to the lower limbs.
A person with weak gluteus medius may exhibit the Trendenlenburg sign during walking - The pelvis will drop on the opposte side. If this situation is not addressed, there will be risks of structural overload to the lumbar spine, sacroiliac joint , hip and knee – and may cause excessive wear and tear at these joints.
A weak gluteus medius can lead to the inward collapse on the knee, placing more pressure on your knee
The figure above shows three different trigger points in the muscle and the pain referral pattern for each. All three of these referral patterns present on a regular basis. Patients come in with low back pain and are surprised to learn it’s not their low back at all, but their glutes. The glute med is constantly firing when we are upright so it makes sense that the muscle is overworked.
INJURIES INFLUENCED BY A POORLY FUNCTIONING OR OVERLOADED GLUTEUS MEDIUS
The injuries include, but are not limited to:
Gluteal Tendinopathy
Gluteal Muscle Strain or Tear
Patellofemoral Joint Pain Syndrome / Anterior Knee Pain
ITB Friction Syndrome
Achilles Tendinopathy
Hamstring Injuries
Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis
Piriformis Syndrome
Trochanteric Bursitis
HOW DO I TRAIN MY GLUTEUS MEDIUS?
Gluteus Medius is most active when performing isolated single-limb exercises.
Research shows that integration of trunk and lumbar stability exercises can further reduce loading onto and requirements of the Gluteus Medius.
We’d recommend the following exercises.
Clams
Bridges with theraband
Ball at the wall squat
Crab walk
Monster walk
SO, AFTER ALL, DO I NEED A BUTT MASSAGE?!
Fun fact, the Gluteus muscles are the largest muscle in the body. If that area gets skipped over your therapist is missing a huge portion of the body. Now you might be totally cool with that, but if you have back pain, knee pain, hip pain or even leg pain? Your glutes may be the reason for it.
Massage in this area will be important to everyone, athletes, arm chair athletes, desk workers, people that stand all day...you get the picture. Muscles all have origin and insertion point that pull and shorten when put under any stress.
If you are a bit shy, always let the therapists know any of your reservations. Glutes can easily be worked on top of the sheet or through clothing. Or the therapist will always drop modestly with a sheet working one side at a time.
So, at your next massage, remember to get the glutes worked on! Your back, legs, hips & knees will thanks you!
MASSAGE + ALCOHOL = BAD IDEA
We all deserve the chance to relax after a long week, and a beer (or three) followed by a soothing massage might sound like a perfect recipe for relaxation.
But if your daydreams involve both a few drinks and a massage therapy session, you should understand that massage therapists don’t really approve the combination of too much booze and a massage.
While there are varying opinions on how long you should wait after drinking to get a massage, massage therapy experts agree that it’s not safe to massage a client when they are drunk, they have a hangover, or they are thinking of drinking a lot after the session.
Before or after massage, drinking can have different effects into your body, and we will explain why is that and why you shouldn't mix this two factors.
How massage affects your body
Massage boosts circulation, pushing the body’s lymph fluid around and helping you to shed excess fluids more quickly. (This is why your therapist will encourage you to drink plenty of water after a massage.)
Massage creates a state of deep relaxation, lowers your blood pressure, reduces levels of stress hormones like cortisol and increases pleasurable hormones like dopamine and serotonin in the body.
These effects of massage alone can be a great thing, but when combined with alcohol can be dangerous. Some massage therapists even report seeing clients get "re-drunk" after a massage. Your time spent in your massage chair should leave you feeling relaxed, healthy, and rejuvenated—not sick or in more pain!
How alcohol affects your body
Alcohol, a diuretic, is well-known for its dehydrating effects, as anyone who’s ever had a hangover headache will tell you.
Alcohol causes your blood vessels to dilate, moving the alcohol through your bloodstream and increasing your blood alcohol level.
Alcohol impairs cognitive reasoning. Alcohol consumption can impair reflexes, limit motor control, and reduce coordination.
Drinking too much weakens the body’s immune system, and a single event of binge-drinking can limit your body’s ability to prevent infections for up to 24 hours
How massage interacts with alcohol
Numbed senses. Alcohol and massage are both relaxing. But Alcohol tends to desensitize the nerve endings and reduce the sensation of touch, making it difficult for you and your massage therapist to judge the best level of pressure and the person may be unable to give appropriate feedback. You want to feel the massage, don’t you?
Amplified drunkenness. Alcohol travels through your bloodstream. (We know, it doesn’t sound as much fun when we say it that way.) Massage increases circulation, which means that alcohol both hits your bloodstream more quickly and remains there longer.
Compromised Judgment & Thinking: We're taught that alcohol affects our judgment. It increasing levels of norepinephrine, the neurotransmitter responsible for arousal and heightened excitement, and an increase in impulsivity as well as a reduction in impulse control. Additionally, alcohol dulls the prefrontal cortex of the brain, the area responsible for decision making and rational thought that also has control over aggressive behavior.
Decreased Motor Activity & Physical Coordination: Because alcohol lowers energy consumption in the cerebellum, which controls your motor activity and overall physical coordination, you can't be certain of your behavior while under the influence. Best to avoid embarrassing—or worse—harmful behavior during an activity that is supposed to be relaxing.
Intensified hangovers. Both massage and alcohol can have a dehydrating effect. This doesn’t just make you thirstier – it can intensify hangover symptoms. There's a reason that drinking water after a massage is highly recommended. Massage is believed to increase movement of fluids, which could also expedite the body's process of breaking down and excreting the alcohol, which in turn could enhance the severity of a hangover and you´ll be thhhhhirsty!
The key is moderation. Alcohol, like massage, has a powerful effect on your body. When you are intoxicated or under the influence, the two don’t mix together in a healthy manner.
Long story short, (too much) alcohol and massage don’t mix well. Feel free to have a glass of wine pre/post-massage, but keep the Oktoberfest-style beer binge for another day!
Neck pain vs Cycling
We left the slopes back in the past and we give way for the mountain bike season during the warmer months in Queenstown.
But… One of the most common injuries/pain related with cycling is neck pain.
This is because it is an activity that requires you to stay for long periods of time in an unnatural position. Cycling stresses your back in a flexed position, this coupled with needing to look where we are going means we compensate leaving the neck in an hyperextended position.
This hyperextended position creates a change on the weight distribution through our muscles and spine. The deep neck extensors are tensed for a long time, blood flow to the area is decreased, becoming fatigued, getting stiffer. This leads to trigger points, muscles spams and potentially a bit of pain.
So, how can we fix neck pain caused by cycling?
Correct fit of your bike.
Professional treatment to ensure muscle and joint flexibility
Regular stretching to maintain a healthy muscle length.
Let’s focus on Regular Stretching…
Regular stretching on cyclist will have immediate effects:
Accelerate recovery: Reducing muscle soreness and stiffness by increasing blood flow, delivering more nutrients to your muscles and removing lactic acid and metabolites.
Increased Oxygen Flow: Decreasing post-ride soreness with the added bonus of promoting cell growth and organ function.
Relaxation: can give both you and your muscles time to relax. With stress or exhaustion, the muscles will begin to tighten. Stretching can encourage a release of endorphins and leave you feeling encouraged.
It will also have cumulative effects:
Prevent Tissue Degradation: Over time and with age, the body starts dehydrating and stiffening. On a cellular level, muscle fibres start developing cross-links with parallel fibers making them stick together. Stretching slows this process by stimulating the production of tissue lubricants and pulling the interwoven cellular cross links back into an ordered state.
Flexibility
Injury Prevention: Stretching keeps the connections strong, treating and preventing injury, improving functionality and longevity.
Better Posture & Aerodynamics: Stretching the right muscles can help correct poor posture both on and off the bike. By lengthening tight muscles that pull areas of the body away from their natural position you can maintain proper posture without the desire to round the back or slouch.
After all of this, you might wonder, what exercises/stretches are good for me?
Here we give you a couple of them that might help!
——————————————————————--Neck Rotation————————————————————————
———————Upper trapezius Stretch ——————————————-Scapula Elevator Stretch————————-
————————————————————20-25 secs each side———————————————————————-
—————————Lateral rotation ————————————-—————-Scalene Stretch———————————-
—————-———3 times per side——————————————-——20-25 secs each side———————————
Feeling a bit cycle sore and want some professional attention? Book a massage therapy today!